-
 Ugly History: The Armenian Genocide
Ugly History: The Armenian Genocide WHG 7.2.1 World War I – explain the causes, characteristics, and long-term consequences of World War I, including the major decisions of the Versailles Treaty.
-
 Research and Resources on American Muslims and the Impact in the United States of Events in Gaza, Israel, and Surrounding Region
Research and Resources on American Muslims and the Impact in the United States of Events in Gaza, Israel, and Surrounding Region
-
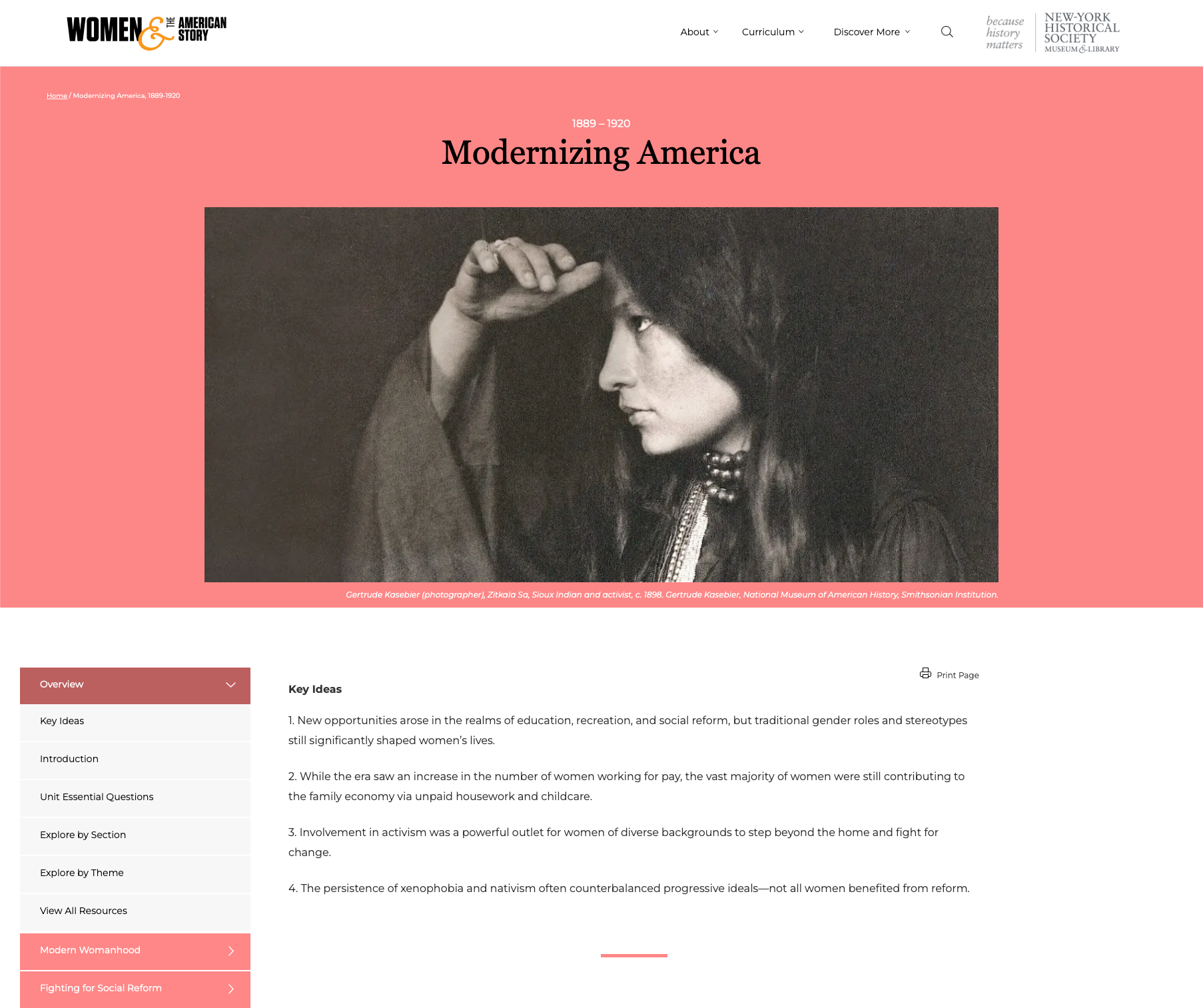 Modernizing America: Women and the American Story History Unit (1889–1920)
Modernizing America: Women and the American Story History Unit (1889–1920) Content wise, this unit goes best with 8th grade and High School USHG Era 6. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
-
 Lawmakers or Lawbreakers? The Crosswhites and Community of Marshall, Michigan
Lawmakers or Lawbreakers? The Crosswhites and Community of Marshall, Michigan 4 – H3.0.3 Use case studies or stories to describe the ideas and actions of individuals involved in the Underground Railroad in Michigan and in the Great Lakes region.
-
 It Starts With Me! Lesson Plan
It Starts With Me! Lesson Plan K – C5.0.1 Describe situations in which they demonstrated self-discipline and individual responsibility.
-
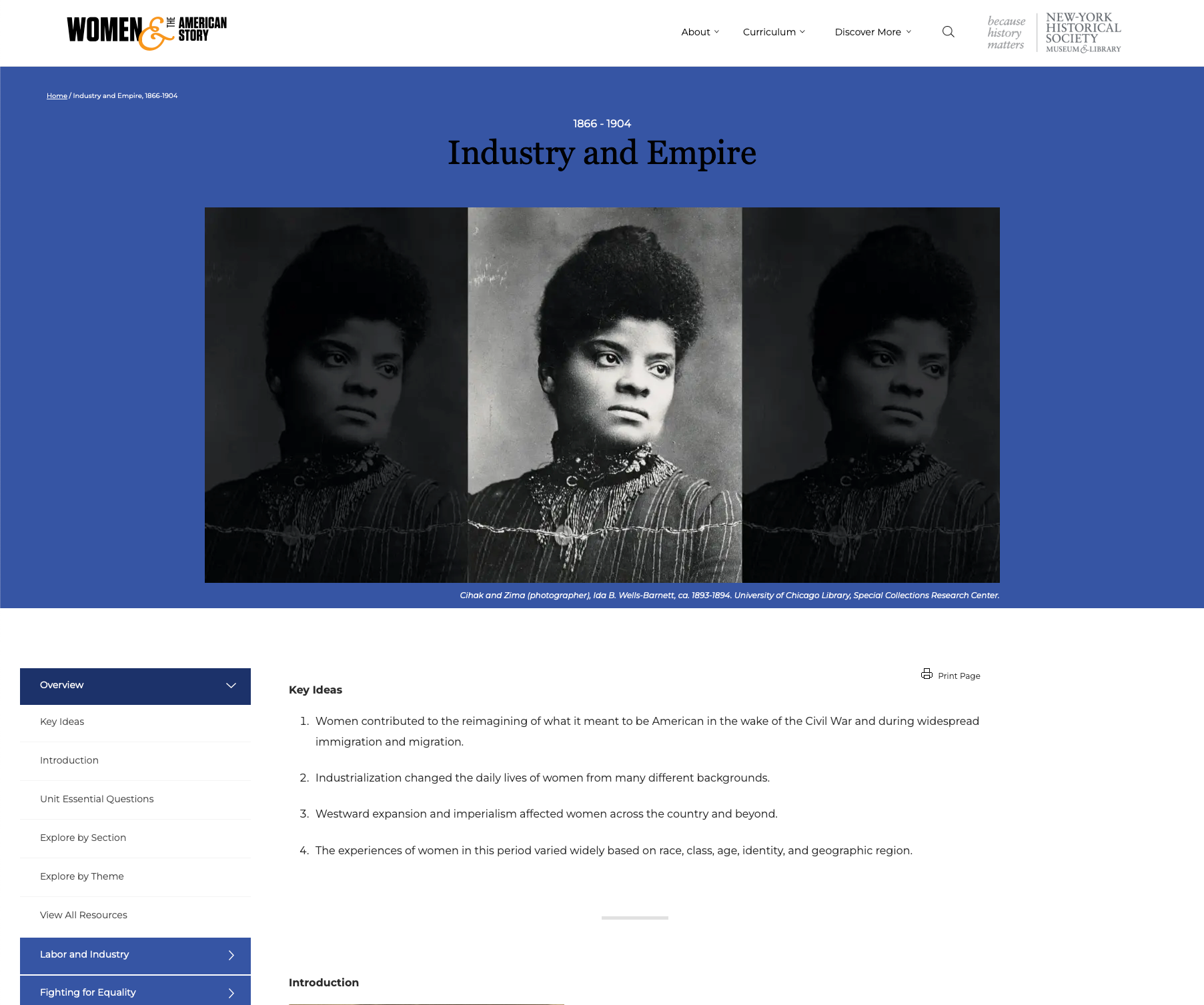 Industry and Empire: Women and the American Story History Unit (1866-1904)
Industry and Empire: Women and the American Story History Unit (1866-1904) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd and 4th grade history, 8th grade USHG Eras 5 + 6 and High School USHG Era 6. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
-
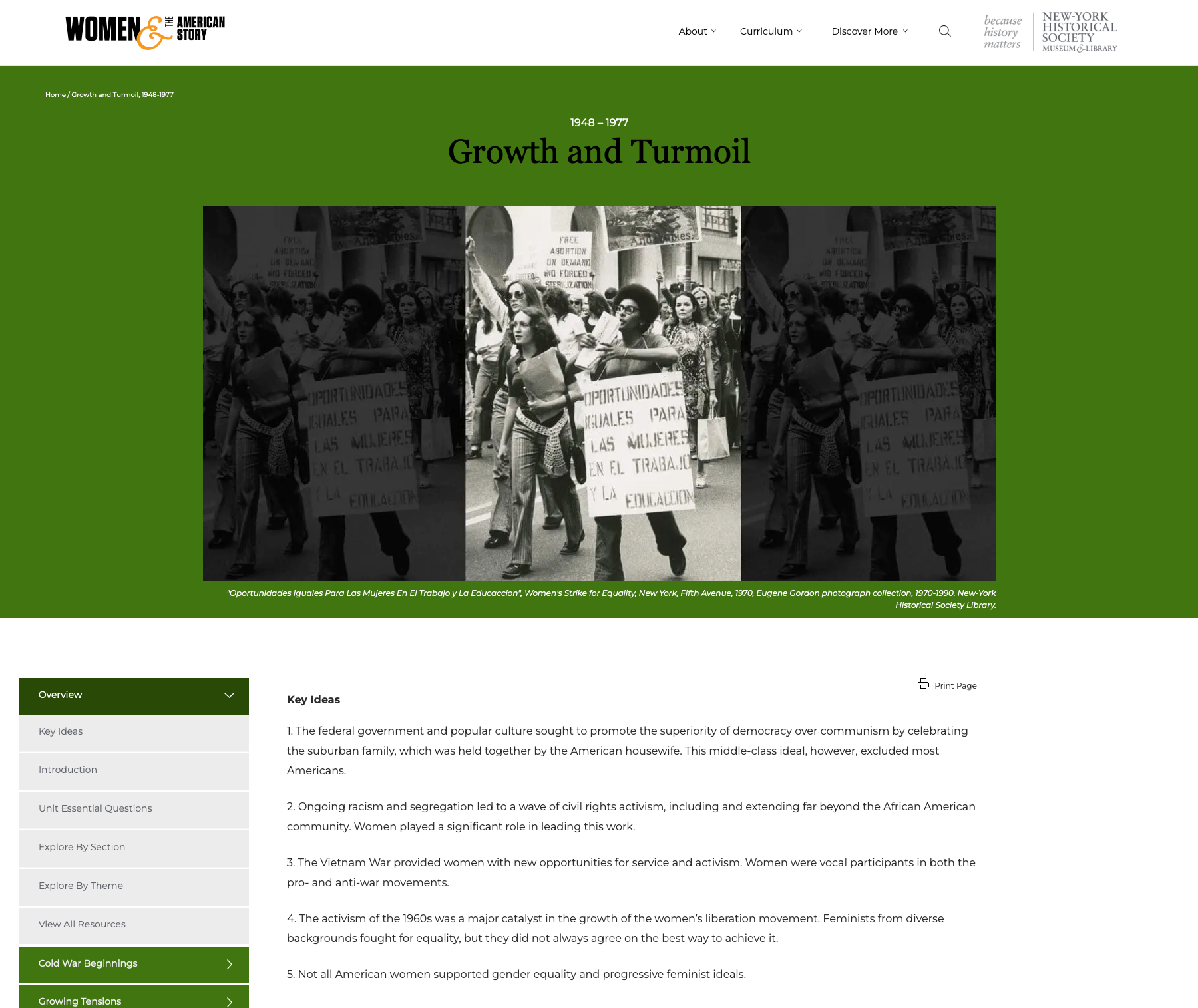 Growth and Turmoil: U.S. History Unit (1948–1977)
Growth and Turmoil: U.S. History Unit (1948–1977) Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 7 + 8. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration.
-
 Famous Author Study #1: Langston Hughes
Famous Author Study #1: Langston Hughes SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS:
7 – H1.2.2 Read and comprehend a historical passage to identify basic factual knowledge and the literal meaning by indicating who was involved, what happened, where it happened, what events led to the development, and what consequences or outcomes followed.
-
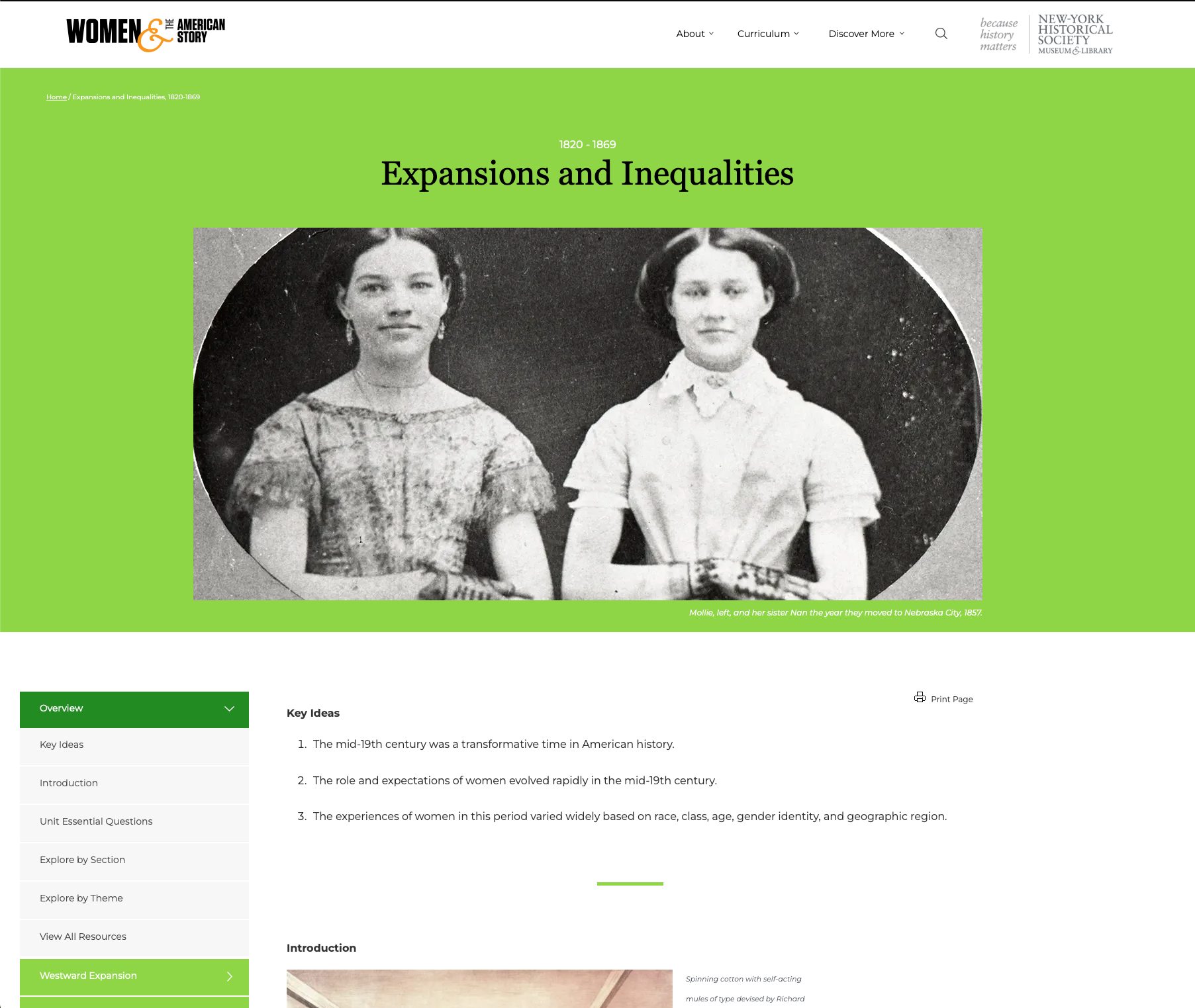 Expansions and Inequalities: Women and the American Story History Unit (1820-1869)
Expansions and Inequalities: Women and the American Story History Unit (1820-1869) Content wise, this unit goes best with 8th grade USHG Eras 4 + 5. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
-
 End of the Twentieth Century Women and the American Story History Unit (1977-2001): A Conservative Turn
End of the Twentieth Century Women and the American Story History Unit (1977-2001): A Conservative Turn Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 8+ 9. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
-
 Early Encounters: Women and the American Story History Unit (1492-1734)
Early Encounters: Women and the American Story History Unit (1492-1734) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd Grade history and 5th grade USHG Eras 1 and 2. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
-
 Confidence and Crises: Women and the American Story History Unit (1920-1948)
Confidence and Crises: Women and the American Story History Unit (1920-1948) Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 6, 7, and 8. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration.
-
 Building a New Nation: Women and the American Story History Unit (1776-1831)
Building a New Nation: Women and the American Story History Unit (1776-1831) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd Grade history and 5th grade USHG Era 3 and 8th grade USHG Eras 3 + 4. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration.
Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
-
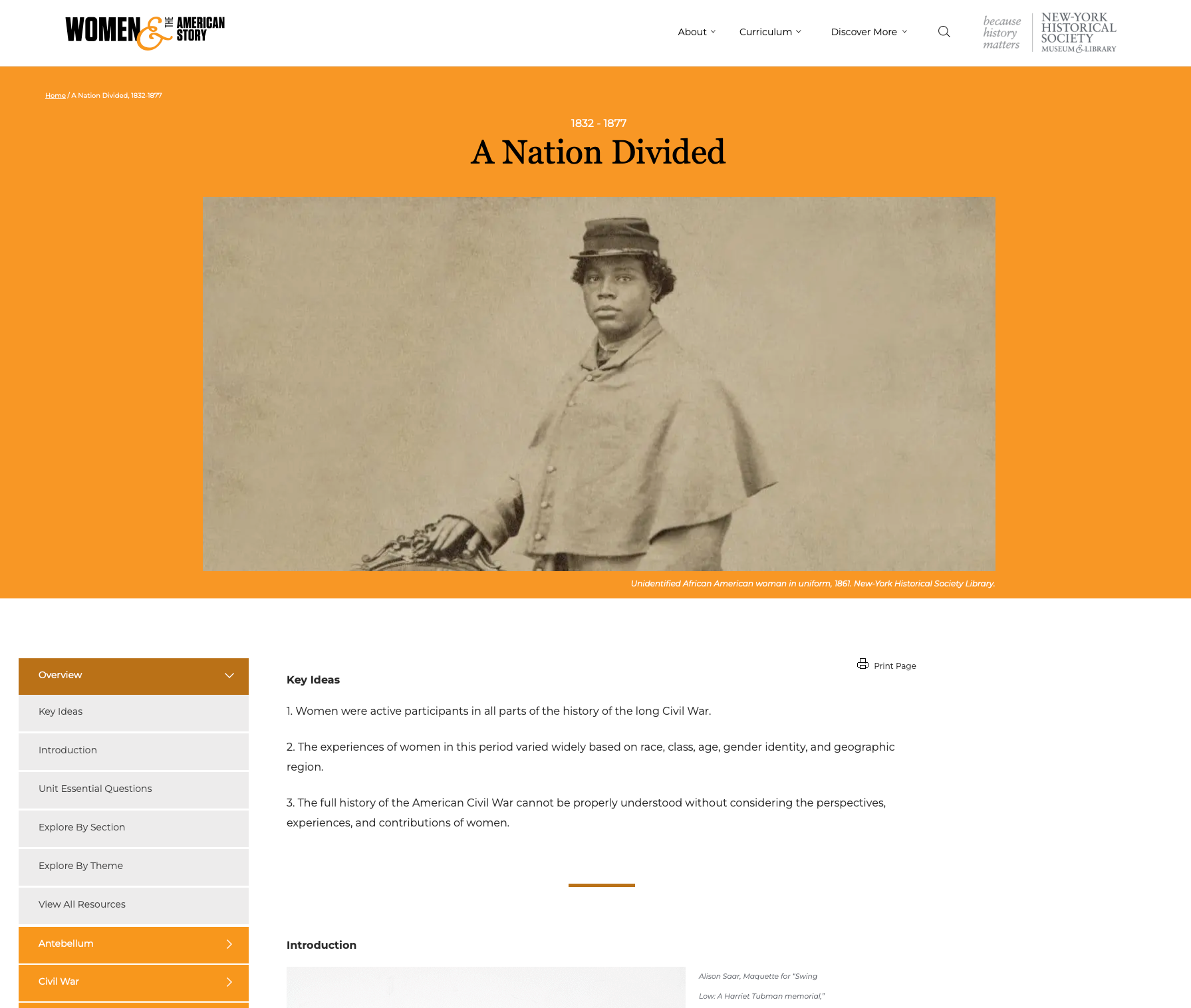 A Nation Divided: U.S. History Unit (1832-1877)
A Nation Divided: U.S. History Unit (1832-1877) Content wise, this unit goes best with 5th grade USHG Era 3 and 8th grade USHG Eras 4 + 5. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
 Ugly History: The Armenian Genocide WHG 7.2.1 World War I – explain the causes, characteristics, and long-term consequences of World War I, including the major decisions of the Versailles Treaty.
Ugly History: The Armenian Genocide WHG 7.2.1 World War I – explain the causes, characteristics, and long-term consequences of World War I, including the major decisions of the Versailles Treaty. Research and Resources on American Muslims and the Impact in the United States of Events in Gaza, Israel, and Surrounding Region
Research and Resources on American Muslims and the Impact in the United States of Events in Gaza, Israel, and Surrounding Region  Modernizing America: Women and the American Story History Unit (1889–1920) Content wise, this unit goes best with 8th grade and High School USHG Era 6. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
Modernizing America: Women and the American Story History Unit (1889–1920) Content wise, this unit goes best with 8th grade and High School USHG Era 6. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards. Lawmakers or Lawbreakers? The Crosswhites and Community of Marshall, Michigan 4 – H3.0.3 Use case studies or stories to describe the ideas and actions of individuals involved in the Underground Railroad in Michigan and in the Great Lakes region.
Lawmakers or Lawbreakers? The Crosswhites and Community of Marshall, Michigan 4 – H3.0.3 Use case studies or stories to describe the ideas and actions of individuals involved in the Underground Railroad in Michigan and in the Great Lakes region. It Starts With Me! Lesson Plan K – C5.0.1 Describe situations in which they demonstrated self-discipline and individual responsibility.
It Starts With Me! Lesson Plan K – C5.0.1 Describe situations in which they demonstrated self-discipline and individual responsibility. Industry and Empire: Women and the American Story History Unit (1866-1904) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd and 4th grade history, 8th grade USHG Eras 5 + 6 and High School USHG Era 6. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
Industry and Empire: Women and the American Story History Unit (1866-1904) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd and 4th grade history, 8th grade USHG Eras 5 + 6 and High School USHG Era 6. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards. Growth and Turmoil: U.S. History Unit (1948–1977) Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 7 + 8. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration.
Growth and Turmoil: U.S. History Unit (1948–1977) Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 7 + 8. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Famous Author Study #1: Langston Hughes SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS: 7 – H1.2.2 Read and comprehend a historical passage to identify basic factual knowledge and the literal meaning by indicating who was involved, what happened, where it happened, what events led to the development, and what consequences or outcomes followed.
Famous Author Study #1: Langston Hughes SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS: 7 – H1.2.2 Read and comprehend a historical passage to identify basic factual knowledge and the literal meaning by indicating who was involved, what happened, where it happened, what events led to the development, and what consequences or outcomes followed. Expansions and Inequalities: Women and the American Story History Unit (1820-1869) Content wise, this unit goes best with 8th grade USHG Eras 4 + 5. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
Expansions and Inequalities: Women and the American Story History Unit (1820-1869) Content wise, this unit goes best with 8th grade USHG Eras 4 + 5. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards. End of the Twentieth Century Women and the American Story History Unit (1977-2001): A Conservative Turn Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 8+ 9. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
End of the Twentieth Century Women and the American Story History Unit (1977-2001): A Conservative Turn Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 8+ 9. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards. Early Encounters: Women and the American Story History Unit (1492-1734) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd Grade history and 5th grade USHG Eras 1 and 2. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
Early Encounters: Women and the American Story History Unit (1492-1734) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd Grade history and 5th grade USHG Eras 1 and 2. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards. Confidence and Crises: Women and the American Story History Unit (1920-1948) Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 6, 7, and 8. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration.
Confidence and Crises: Women and the American Story History Unit (1920-1948) Content wise, this unit goes best with High School USHG Eras 6, 7, and 8. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Building a New Nation: Women and the American Story History Unit (1776-1831) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd Grade history and 5th grade USHG Era 3 and 8th grade USHG Eras 3 + 4. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
Building a New Nation: Women and the American Story History Unit (1776-1831) Content wise, this unit goes best with 3rd Grade history and 5th grade USHG Era 3 and 8th grade USHG Eras 3 + 4. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards. A Nation Divided: U.S. History Unit (1832-1877) Content wise, this unit goes best with 5th grade USHG Era 3 and 8th grade USHG Eras 4 + 5. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.
A Nation Divided: U.S. History Unit (1832-1877) Content wise, this unit goes best with 5th grade USHG Era 3 and 8th grade USHG Eras 4 + 5. There are opportunities for geography, economics, and civics integration. Which standards are best will depend on the resources you include, how you include them, and the grade you teach. That said, we do recommend these resources for all grades to help develop historical thinking and inquiry skills described in the K - 12 standards.